Cancer: An Overview

Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. It can affect various parts of the body and is classified based on the tissue or organ where it originates. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes. Common types of cancer include:
-
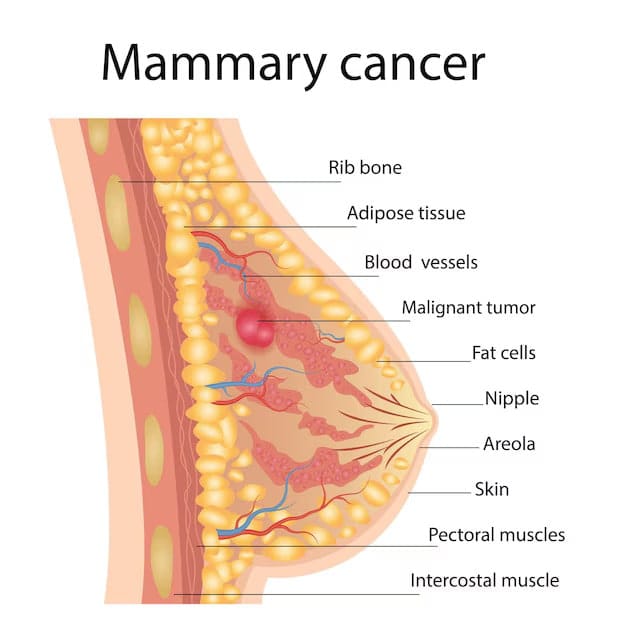
Breast Cancer: A malignant tumor that develops in the breast tissue, often presenting as a lump or changes in breast shape or texture. Regular screenings and awareness of family history are important for early detection.
-
Thyroid Cancer: A type of cancer that originates in the thyroid gland, usually presenting as a nodule or swelling in the neck. It often has a favorable prognosis, especially when diagnosed early.
-
Skin Cancer: The most common type of cancer, typically arising from excessive sun exposure. The main types include melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Regular skin checks can help detect changes early.
-
Soft Tissue Sarcoma: A rare type of cancer that develops in soft tissues such as muscles, fat, nerves, and blood vessels. Symptoms can vary widely depending on the tumor's location.
-
Gallbladder Cancer: A rare cancer that forms in the gallbladder, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to vague symptoms. Risk factors include gallstones and chronic inflammation.
-
Stomach Cancer: Also known as gastric cancer, this type begins in the stomach lining and may present with symptoms like weight loss, stomach pain, and indigestion. Early diagnosis is critical for effective treatment.
-
Pancreatic Cancer: A highly aggressive cancer that originates in the pancreas. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, weight loss, and jaundice, often leading to late-stage diagnosis.
-
Colon Cancer: Cancer that starts in the colon (large intestine), often linked to genetic factors and lifestyle choices. Regular screening, such as colonoscopy, is vital for early detection.
-
Rectal Cancer: Similar to colon cancer, this type occurs in the rectum and can present with changes in bowel habits or rectal bleeding. Early detection improves prognosis.
-
Cervical Cancer: Cancer of the cervix, often linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. Regular Pap smears can help detect precancerous changes and reduce the risk of developing invasive cancer.
Understanding these cancer types, their symptoms, and the importance of early detection can help improve awareness and outcomes for those affected. Regular screenings and healthy lifestyle choices play a vital role in cancer prevention and management.